Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Physiotherapy Treatment for COPD
Goals of treatment for COPD include:
- Relieving symptoms
- Slowing progress of the disease
- Improving exercise tolerance (ability to stay active)
- Preventing and treating complications
- Improving overall health
COPD is not a reversible condition and has no cure yet, but conservative treatment for COPD can slow its progression (smoking cessation being the most important).
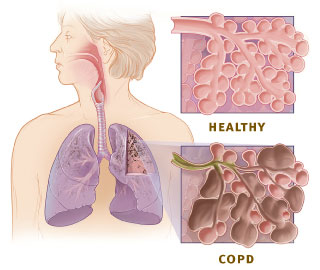
What is COPD?
COPD or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a progressive disease that makes it hard to breathe. COPD can cause coughing that produces large amounts of mucus (a slimy substance), wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and other symptoms. Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Most people who have COPD smoke or used to smoke. Long-term exposure to other lung irritants, such as air pollution, chemical fumes, or dust, also may contribute to COPD. COPD include Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema.
Physiotherapy treatment for COPD
Aims of COPD Therapy
- To remove excess bronchial secretion and reduce the airflow obstruction.
- To establish the coordinated pattern of breathing
- To promote relaxation and improve posture
- To improve the mobility of thorax, shoulder girdle and neck
- To increase the exercise tolerance
- To encourage a full and active life style.
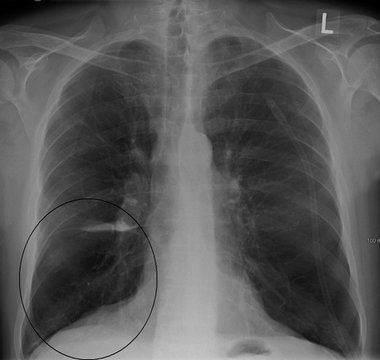
COPD X-RAY showing BULLA
Means of COPD Treatment
1. Postural Drainage (P.D) is necessary for all patients. In chronic bronchitis regular postural drainage should be given. In case of acute emphysema, postural drainage is not necessary but in an infection episode, where sputum may be present PD may be needed. The optimum position must be established with individual and advice for postural drainage at home.
Clapping and Shaking are effective over the affected lung segments and help to loosen and move the secretions to central airways during expiration. Then ask the patient to take 2-3 coughs to remove the secretions out. If the patient is unable to clear the secretions which are accumulated in lungs, then increased ventilation and humidification by IPPB conjoint with P.D are provided. This is very effective for patient. But in presence of emphysematous bullae, it is contraindicated because of risk of causing pneumothorax.
In case of acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis the physiotherapy must be given vigorously. IPPB has great value in this case. It is given with mask to improve ventilation. It is important to observe the chest wall movement and level of consciousness. The patient should be observed for any signs of drowsiness after taking the treatment. Assisted ventilation with vigorous chest shacking and postural drainage are more effective. A ventilatory mask providing controlled oxygen therapy is usually required.
2. Breathing exercises should be given in a correct way in treatment for COPD. The main emphasis is given on diaphragmatic breathing with relaxed expiration. The diaphragmatic breathing with decreased upper chest movements and relaxed shoulder girdle is preferred. Expansion of basal lung segments are taught to ventilate these areas.
Pursed lip breathing with prolonged expiration is given as treatment for COPD especially in presence of emphysematous bullae.
3. Posture Correction Patient should be taught to attain maximal relaxation of the upper chest as well as movements of lower chest. The main emphasis is on relaxed and controlled diaphragmatic breathing. For maintaining posture the patient should not be kept with forward head and rounded shoulder.
4. Thoracic mobility exercises are given along with shoulder girdle movements. Free active exercises for whole spine to prevent kyphosis and fixed inspiration.
Important copd exercise in sitting is trunk turning with loose arm swinging in rotation for relaxation. It is also essential to emphesise postural awareness so that the patient practices shoulder girdle retraction and lateral rotation of arm.
Read more about COPD Treatment at Mayoclinic
5. These patients should be as mobile and active as possible. Their exercise tolerance may be increased by gradually increasing the distances walked both on the flat and upstairs or slopes while practising breathing control. A graduated exercise programme can also be given to these patients during the later part of their stay in hospital and should be continued at home.
6. In daily life style patient should avoid smoking and encouraged to keep fit and eat sensibly. For gaining relaxation, swimming helps very much. Jerky and quick movements should be strictly avoided.
Return from treatment for copd to chest physical therapy
Return from treatment for copd to Home page
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

