Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
chronic bronchitis treatment
The main goals in the Chronic Bronchitis Treatment is to keep the airways open and functioning properly, to help clear the airways of mucus to avoid lung infections and to prevent further disability.
What is Chronic Bronchitis?
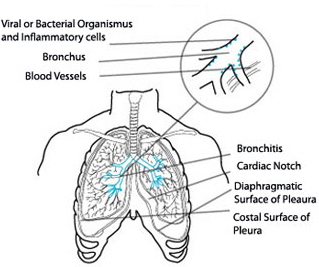
Chronic Bronchitis is a disease characterized by cough productive of sputum on most days for at least three consecutive months of each year for at least two successive years.
This definition shows that other causes for sputum and cough production such as bronchiectasis and tuberculosis have been excluded. Chronic bronchitis causes inflammation and irritation of the airways, the tubes in lungs where air passes through. When the air tubes are inflamed and irritated, thick mucus begins to form in them. Over time, this mucus plugs up the airways of the lungs and makes breathing difficult.
Unlike acute bronchitis, chronic bronchitis is irreversible and its path is one of frequent recurrences.
Chronic Bronchitis Causes
This is more common in middle to late adult life and occurs in men more than women. Ratio is 5:1. Cigarette smoking is a major factor. Atmospheric pollution and coal dust are other important factors.
This disease is more common in urban areas than rural areas. Additionally, allergies, and infection are known factors that can cause exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. In fact, people who are diagnosed with chronic bronchitis are more likely to develop recurring infections in the lungs.
Chronic Bronchitis Pathophysiology
The main morphological feature in chronic bronchitis is hypertrophy of mucous gland tissue in the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles. There is considerable increase in the mucous gland content in the submucosa of the airways and a great increase in the number of goblet cells especially in the bronchioles. Associated with this mucous gland hypertrophy there is thickening of the mucous membrane and excessive mucous production together with some bronchial wall muscle hypertrophy. The end result of these changes is impairment of removal of inhaled particles and infection in mucous within the tracheo-broncheal tree leading to sputum retention and increase in airways obstruction. Culture of sputum from patients with chronic bronchitis usually yields a growth of Haemophilus influenzae or Streptococcus pneumoniae. The number of these organisms is often increased during acute exacerbations.
Chronic Bronchitis Symptoms
People with chronic bronchitis may experience the following symptoms:
- Long-term cough
- Increased mucus production
- Dyspnea
- Edema and weight gain (often occur as side effects of medication)
- Frequent clearing of the throat
The cough that accompanies chronic bronchitis is sometimes brought on by cold weather, dampness and things that irritate the lungs, such as fumes or smoke. Usually, the patient will have a history of smoking and repeated infections of the lungs.
Chronic Bronchitis Diagnosis
The presence of a productive, long-term cough that lasts 3 months out of the year for 2 consecutive years points doctors in the diagnostic direction of chronic bronchitis.
A diagnosis of chronic bronchitis is made by obtaining a complete history, including family, environmental and occupational exposure, and smoking history. Proper and early diagnosis is essential for chronic bronchitis treatment. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Pulmonary function tests
- Chest X-ray
- Arterial Blood Gases
- Complete blood count
- Spirometry
- Serum alpha1-antitrypsin
Prevention and Screening
The best way to keep from getting chronic bronchitis and other lung problems is not to smoke.
Smoking can cause a variety of lung diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cancer. Smoking can also make chronic bronchitis get worse more quickly, increase susceptibility to other illnesses, and shorten life. People who are exposed to secondhand smoke are also at greater risk of illness and disease.
Avoid inhaled irritants, such as air pollution or workplace dust or fumes. Also, limit exposure to indoor pollutants by using fewer aerosol deodorants, insecticides, and hair sprays.
Chronic Bronchitis Treatment
The goal of chronic bronchitis treatment is to help you live more comfortably and slow the progression of your disease.
1. First to minimize the irritation of bronchus: Patient should be urged to give up smoking, avoid dusty, damp and smoky atmosphere as first step towards Chronic Bronchitis Treatment. If patient is obese he should be advised to loose the weight.
2. Subside the infection: To prevent further damage to airways the infection must subside as soon as possible. Oral antibiotic drugs should be given for a course of 5-7 days.
Ampicillin-500 mg 6 hourly
Cotrimazole-2 tablets B.D
Polyvalent influenza vaccine should be given in each winter season.
3. Control Bronchospasm: To relieve the airway obstruction, certain drugs like salbutamol can be given, which is good bronchodilator and it can treat breathlessness also along with Chronic Bronchitis Treatment.
4. Oxygen Therapy: It should be given when the patient is hypoxic and prone to respiratory failure. It is given through ventimask with careful monitoring of blood gas level.
5. Possible congestive heart failure care: In later stage of chronic bronchitis there are chances of congestive cardiac failure, then diuretic therapy and potassium supplements will be given.
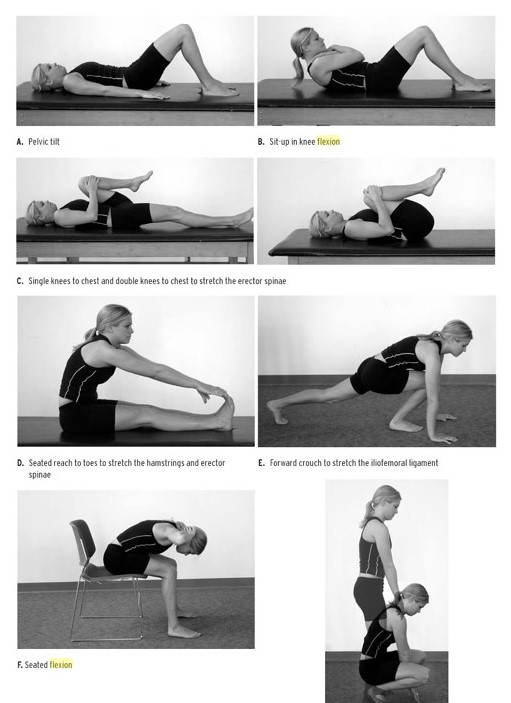
6. Physical Therapy: Certain postures, methods of coughing, and ways of striking the chest and back can help keep air passages clear of mucus.
Certain techniques can help people with bronchitis to keep their airways clear of mucus. Physical therapist will be able to teach these techniques to patient (and a family member or caregiver):
- Postural drainage - prescribed positions that allow gravity to assist in draining secretions from different areas of the lungs, making secretions easier to cough out
- Chest percussion - lightly clapping your chest and back to help dislodge secretions
- Controlled coughing - techniques that help you cough up mucous.
7. Surgery: Lung transplants and lung reduction surgery are used only rarely in Chronic Bronchitis Treatment.
My final words are:- Work with your clinician to find Chronic Bronchitis Treatment that is best for you.
Further Reading
- Chronic Bronchitis. Medline Plus
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Chronic Bronchitis. PDR Health
- Kim V, Criner GJ. Chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb 1;187(3):228-37.
- D Newton. Physical therapy in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J. Feb 3, 1979; 1(6159): 344.
- Wollmer P, Ursing K, Midgren B, Eriksson L. Inefficiency of chest percussion in the physical therapy of chronic bronchitis. Eur J Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;66(4):233-9.
- Bellone A, Lascioli R, Raschi S, Guzzi L, Adone R. Chest physical therapy in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis: effectiveness of three methods. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000 May;81(5):558-60.
- Burford JG, George RB. Respiratory physical therapy in the treatment of chronic bronchitis. Semin Respir Infect. 1988 Mar;3(1):55-60.
- Bronchitis. Physiopedia
Return from Chronic Bronchitis Treatment to Chest Physical Therapy
Return from Chronic Bronchitis Treatment to Home Page
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

