Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Patellar Tendinitis or Tendonitis
Patellar tendinitis or ‘jumpers knee’ is a condition that results from an inflammation of the patellar tendon. The patellar tendon is the structure that connects the patella (knee cap) to the tibia (shin bone). Taking a closer look at anatomy, the knee cap is a small floating bone (sesamoid bone) which attaches the quadriceps to the tibia through the patellar tendon. Hence the patellar tendon being a continuation of the bulky quadriceps muscle is pivotal in the way you move your leg. It helps the quadriceps muscle extend the lower leg so that you can kick a ball, jump in air or push the pedals on your bike.
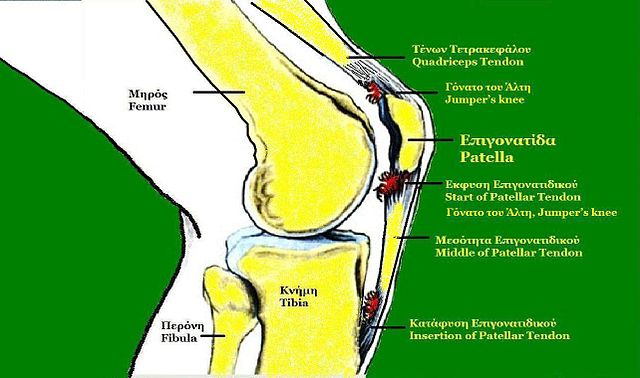
Etiology of Patellar Tendinitis
The commonest cause of
jumpers knee is overuse. This occurs frequently in jumping sports such as basketball and volleyball and hence it is often referred to as ‘jumpers knee.’ However it can occur with sports such as running and soccer too. A less common cause is due to direct injury to the tendon.
The inflammation can be a result of numerous factors. Here are some of the causes which lead to patellar tendonitis:
Training Errors
Biomechanical Factors
- Reduced flexibility of the thigh muscles namely the quadriceps and the hamstring muscles
- Muscle imbalance, if some muscles in your leg are much stronger than others
- Patella alta, a condition in which the knee cap is structurally much higher than the knee joint
- Overweight
- Foot conditions, either a flat foot or a raised arch can impose high strain on the patellar tendon
Symptoms of Patellar Tendinitis
The symptoms of patellar tendonitis are pain and occasionally a swelling over the patellar tendon. Pain is usually sharp during the sporting activities such as jumping or running and persists as a dull ache after the activity. Initially the pain might be present only during the start or after completing the sport or work out which then worsens to becoming more constant in nature. Everyday activities such as climbing up and down stairs might be painful too. Pain on pressing directly over the patellar tendon is a characteristic feature in examination.
Investigations
An X-ray might provide additional information of a bone spur and an MRI is needed in more chronic cases to rule out tendon degeneration.
Treatment of Patellar Tendinitis
Read about Patellar Tendonitis on Wikipedia
Treatment of patellar tendonitis is usually conservative, and is briefly discussed below:
Rest:
Not necessarily meaning to stop all activities but only those that involve straining the patellar tendon i.e. Jumping and running
Correcting Body Mechanics:
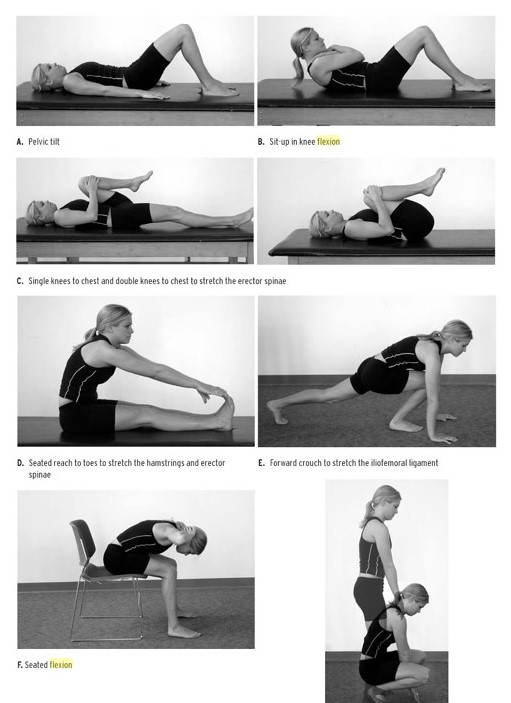
- Stretching tight thigh muscles to equalize force distribution in the leg muscles
- Strengthening the quadriceps muscle, particularly in an eccentric fashion
- Proper form in take off and landing techniques in sport
Patellar Tendon Strap:
Strapping or taping techniques might help take off pressure from the patellar tendon and help in further aggravation as well as pain relief
Orthotics:
Foot orthotics to support the arch for better shock absorption in jumping and other impact sport
Electrotherapy:
- Physiotherapy treatments such as ultrasound and, laser might help in pain relief during the acute phase of healing
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy using sound waves to heal the tendon
Medications such as NSAIDS and corticosteroids are used to settle the initial acute healing phase
If the symptoms persists beyond 6 months after attempting conservative treatment then surgery can be discussed. There is little research available on the best surgical options for patellar tendonitis so the procedure depends largely on the surgeons discretion.
Return from Patellar Tendinitis to Home Page
Return from Patellar Tendinitis to Orthopedic Physical Therapy
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

