Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Snapping Hip Syndrome
Snapping hip syndrome is a condition where one feels ’snapping’ sensation in hip while walking, getting up from a chair or while swinging the leg around. This is accompanied by popping or snapping noise. Pain and discomfort is felt in some cases. This pain decreases with rest and diminished activity. Hip snapping can either be external (lateral) or internal.
The condition is also known as
- iliopsoas tendinitis,
- coxa saltans and
- dancer’s hip.
Types of snapping hip syndrome
Lateral snapping hip is felt at the outside of the hip and is caused by the muscle fibres of Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL) or Gluteus Maximus flicking across the greater trochanter (bony protrusion on the upper part of the femur (thigh bone). The clicking feeling is usually not painful.
Internal snapping hip is caused by the Iliopsoas muscle as it flips across the Iliopectineal eminence (front part of the pelvis). This form is more likely to produce pain.
Causes of snapping hip syndrome
Snapping hip has been attributed to multiple mechanisms associated with the skeletal architecture of the hip and pelvis and with the muscles, tendons, and ligaments around the hip. Snapping hip has been described according to the location of the mechanism as external, internal, or posterior. Despite the many descriptions of possible mechanisms, the most common causes of snapping hip include either subluxation of the iliotibial band over the greater trochanter or sudden movement of the iliopsoas tendon over the iliopectineal eminence.
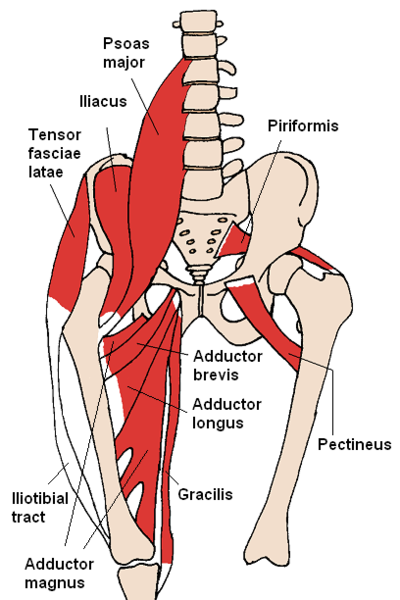
External snapping is primarily caused by subluxation of the iliotibial band over the greater trochanter of the femur. It has also been described as a snapping of the outer border of the gluteus maximus over the greater trochanter.
Internal snapping occurs by one of several mechanisms.
- The most common cause is the iliopsoas tendon sliding over the iliopectineal eminence, resulting in a snap or pop. This typically occurs while the hip suddenly moves into extension from a flexed and externally rotated position.
- The iliopsoas tendon also may produce snapping with sudden movement over the anterior inferior iliac spine or possibly the bony ridge on the lesser trochanter.
- Less common causes of internal snapping hip syndrome include movement of the iliofemoral ligaments over the femoral head or anterior capsule of the hip.
Posterior snapping hip syndrome is uncommon and is caused by movement of the long head tendon of the biceps femoris over the ischial tuberosity.
People who are in risk of developing snapping hip syndrome
- Athletes, due to repeatedly forced movements
- Ballet dancers
- Gymnasts
- Horse riders
- Track and field athletes
- Soccer players
- Excessive weightlifting or running
Snapping hip is mostly seen in people of age group of 15 to 40 years.
Snapping Hip Syndrome Symptoms
The most identifiable symptom is a snapping sound which can be heard when the hip joint is flexed or stretched for moving legs during activities like cycling, walking or kicking. This goes once the activity is stopped. The location of the snapping sensation depends on the connective tissue which has been damaged. In most cases of snapping hip, the thick, dense tendon named iliotibial band located at the side of the leg gets affected and the snapping occur at the side of the hip. When the iliopsoas located at the front part of the hip joint changes its position, then the popping sound is felt on the frontal hip region. Based on the position of the affected joint structure, snapping hip is classified into two different types. They are: intra-articular which means inside joint and extra-articular which means outside joints.
Initially, it does not give any painful symptoms. However, with passage of time, as the connective tissue start wearing out, one experiences sharp hip pain along with the snapping. Usually, this pain disappears as soon as the repetitive joint movement is stopped. If this mild condition is left untreated, then the hip joint pain get aggravated and swelling and tenderness can be felt in the area.
Diagnostic Imaging
- Ultrasound during hip motion may visualize tendon subluxation and any accompanying bursitis when evaluating for iliopsoas involvement in medial extra-articular cases.
- MRI can sometimes identify intra-articular causes of snapping hip syndrome.
Snapping Hip Syndrome Treatment
As long as snapping hip does not give any pain, the condition does not require any treatment. A little bit of correction or modification in the hip joint movements during activities can bring about improvement. However, as soon as it hurts you must stop any such action that tend to aggravate the pain. You have to provide rest to the hip joints as much as possible. If there is swelling, then ice application can reduce the swelling.
Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (or NSAIDs) can give temporary relief to the pain. For a more severe pain and inflammation, doctors administer cortisone injections. As the pain subsides, doctors recommend physical therapy. A physical therapist suggest some snapping hip exercises which involves mild stretching of the affected tendons. Standing side bends and crossed leg side bends are some of them. Deep tissue massage of thigh and buttock muscles is also effective for hip pain relief. In some serious cases, where the tissue is badly damaged, these conservative methods of treatment does not yield any results. Therefore, surgery has to be conducted. During surgical operation, a small incision is made in the hip area and the damage is repaired.
Those who are at the risk of developing snapping hip can prevent it with the help of suitable hip exercises. They are mainly some hip stretches that makes the muscles of the area strong and flexible. These hip flexibility exercises should be performed prior to any strenuous activity involving the hips. Thus the chances of displacement of the tissues because of abrupt hip movements is lowered to a great extent.
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation
There are several effective techniques for alleviating the pain of snapping hip in the acute phase:
- deep massage over the outside of the thigh and buttocks muscles
- icing
- gentle stretching
- Physical therapy modalities like Ultrasound and phonophoresis are commonly used in the acute phase when caring for patients with snapping hip syndromes.
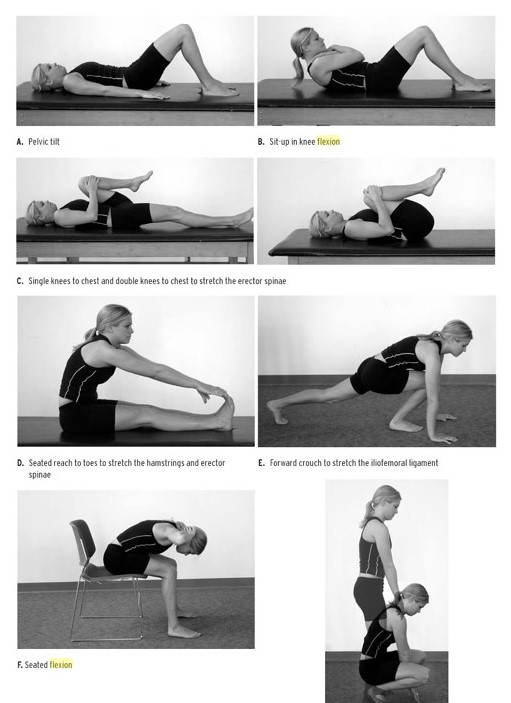
Exercises for snapping hip syndrome
Both active and passive stretching exercises that include hip and knee extension should be the focus of the program.
- Myofascial release techniques to any surrounding tight muscles. Prescribe pelvic stability exercises .
- Stretching the hip into extension and limiting excessive knee flexion avoids placing the rectus femoris in a position of passive insufficiency, thereby maximizing the stretch to the iliopsoas tendon.
- Strengthening exercises for the hip flexors may also be an appropriate component of the program.
- Education, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug regimen, as well as activity modification or activity progression (or both) may be used. Once symptoms have decreased a maintenance program of stretching and strengthening can be initiated.
- Light aerobic activity (warmup) followed by stretching and strengthening of the proper hamstring, hip flexors, and iliotibial band length is important for reducing recurrences.
Conservative measures generally resolve the problem in 6 to 8 weeks.
Prevention
Read Research articles about Snapping Hip in PubMed
The primary goal for prevention of snapping hip syndrome is maintenance of good flexibility and strength in the hip and pelvis. The key to preventing snapping hip is a balanced stretching routine. Stretch both the abductors and adductors evenly. The abductors are the hip muscles that move the leg away from the midline of the body. The adductors are the hip muscles that bring the leg back to the midline of the body. In their 1987 study, Reid et al. recommended that ballet dancers include a structured iliotibial-band stretch as part of their warm-up and stretching routines.
Return from Snapping Hip Syndrome to Sports Physical Therapy
Return from Snapping Hip Syndrome to Home Page
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

