Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Varicose Ulcers
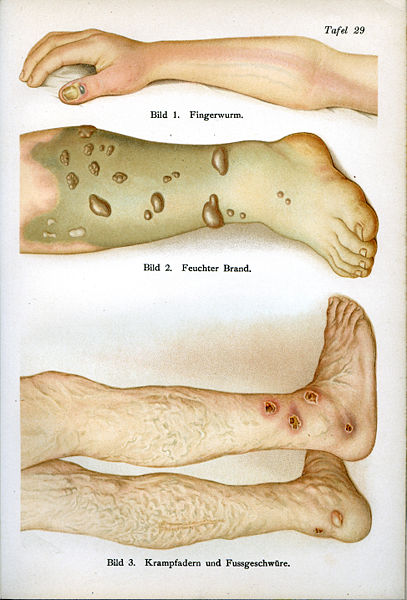
Varicose ulcers/Venous ulcers result from loss of epithelial cells causing exposure of the underlying tissue due to improper functioning of valves in the veins usually of the legs.
- They are found more commonly in females compared to males.
- Common age group is 50-70 years.
- site- Lower 2/3rd of the lower leg (slightly higher on anterior and medial aspect) and on parts of foot not supported by shoe.
- size-Variable. 18 to 20 cm square on the lower leg is quite common. Occasionally may become very large and encircle the leg.
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
- 1-Venous and lymphatic congestion associated with varicose vein or DVT.
- 2-Prolonged standing during work.
- 3-Poor personal hygiene and malnutrition.
PATHOLOGY
- -Due to failure of venous pump and lack of pumping action by calf muscles,there is venous congestion.This leads to increased exudate and decrease in blood flow.
- -Nutrition of the tissue is decreased and the skin is devitalized.
- -Cells necrose and skin breaks down. There is insufficient oxygen and nutrition to promote healing and the area remains open.
- -Bacteria may invade the area or the dead cells may irritate the normal tissues, causing inflammation and the ulcer spreads.
If the (i) Chronic venous congestion is decreased and (ii) The circulation, bringing oxygen and nutrition to the area is improved together with the removal of any infection and the mobilizing of the soft tissues, the ulcer heals with the formation of the scar tissue.
CLINICAL FEATURES
1-Floor of the ulcer may be-
- a) PALE and ANAEMIC with watery discharge. Indolent ulcer -static and non healing ulcer.
- b) GREEN or YELLOW DISCHARGE-infected ulcer.
- c) PINK,BUBBLY WITH RED SPOTS-granulating ulcer.
2-Edge of the ulcer (boundary between floor and the surrounding skin) may be-
- a) Well defined,straight,red and shiny-spreading ulcer.
- b) Hard, oedematous and over hanging floor-chronic ulcer.
- c) Shallow, slopping out from the floor-healing ulcer.
3-Base of the ulcer may show-
- a) Gross induration (hardening),the extent of which varies according to the severity and duration of the ulcer.
- b) Pigmentation due to breakdown of RBC's .
- c) Poor circulation.
- d) Coarse skin texture with heavy scaling or papery thin and eczematous tissue.
4-Edema of the base of the ulcer and the foot and ankle to shoe line.
5-Pain in infected ulcers. Increases with walking.
6-Decreased range of motion of the ankle and foot.
7-Muscle weakness and atrophy mainly of the calf muscles and loss of pumping action.
8-Push off missing in the gait.
VARICOSE ULCERS TREATMENT/VENOUS ULCERS TREATMENT
- a) conservative
- b) surgical
Since physical therapist's role is limited to conservative treatment of skin ulcer, we here discuss only conservative management.
Aims of Conservative/Physiotherapy Management of venous ulcer-
- 1- To relieve pain.
- 2- To relieve congestion and edema.
- 3- To improve general circulation of lower limb.
- 4- Soften induration of lower leg specially around the ankle area.
- 5- Mobilize joints of lower limb and improve strength.
- 6- To improve the condition of the skin of the lower limb.
specific local aims-
- 1- Increase circulation to the ulcer to promote healing.
- 2- Clear any infection.
- 3- Reduce edema and induration around the ulcer.
- 4- Free adherent ulcer from underlying tissue.
METHODS OF TREATMENT OF VARICOSE ULCER
Read more about Varicose Ulcers at nhs.uk
1-soft tissue techniques-
- Remove the bandage and dressings, clean wound and cover with gauge swabs.
- Elevate leg to an angle of 45 degree at hip to aid venous drainage.
- Soft tissue techniques to the whole limb to decrease edema.
Effleurage, slow deep kneading. Picking up wringing the thigh. Special attention to dorsum of foot, region of tendo-calcaneus and behind the malleoli (as in this area vascular supply is less). Thumb kneading over the tibialis anterior muscle.
The region of the ulcer is next treated with finger and thumb kneading to soften the induration, working inward from the periphery to the edge of the ulcer.
2-UVR
a) FOR INFECTED ULCERS- to destroy the micro-organism and increase the circulation to the area. Most commonly used is kromayer lamp and mercury vapour lamp.
To the base of the ulcer-E4 dose or E4x2 dose. Repeat 2-3 times per week until ulcer is clear of infection.
For edges of varicose ulcers when no infection then E1 or E0 dose to promote healing. Repeat daily.
b) FOR HEALING ULCER As ulcer heals,it grows inwards from the edge or outwards from the middle. UVR is given to promote granulation tissue formation.
For floor of the varicose ulcers E1 for shallow ulcer and E2 for deep ulcers. E1 and E0 to surrounding skin. E0 and E1 is repeated daily and E2 is given twice weekly.
These dosages can be given with cellophane filters which cut out the abiotic (UVC rays) and stimulate the growth of the granulation tissue.
c) FOR INDOLENT ULCERS UV rays are given to stimulate the circulation. Absorption of rays produces hyperemia in the congested area and produce an increased exudate.
E3 to the floor with edges screened. E1 or 2to the edges and surrounding skin. As varicose ulcer improves, base becomes pink and vascular E3 reduced and treatment for healing ulcer is given.
3-ULTRASOUND THERAPY
a) It promotes healing of the ulcer.
b) Soften the induration.
c) Increase vascularity in the surrounding tissue.
3MHz, 0.25-o.5 W/cm square for 5-7 minutes in pulsed mode for small ulcer and continuous mode for large ulcer. 1W/cm square if chronic indurated areas in lower leg.
Ultrasound is contraindicated in infected ulcers or in DVT.
4-LASER THERAPY It increases vasodilation and increase the number of fibroblasts.
1Joule intensity at the margins and 2-4 J/cm square at the floor. Cluster probe can be used for varicose ulcers.
Return from varicose ulcers to skin disorders
Return from varicose ulcers to home
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

